HTML Table is defined with the <table> tag.
Syntext:
<table>
// Table Content
<table/>
For table heading, we use <th> tag.
Syntext:
<th>//table heading</th>
For rows, we use <tr> tag.
Syntext:
<tr>//table row</tr>
For columns/cell, we use <td> tag.
Syntext:
<td>//table column</td>
For more clarity, let's create an example:
<table>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Age</th>
</tr>
</table>
In the above example, we first start our table using the <table> tag. After that, we need a row for that we start our <tr> tag. We can't close our <tr> tag now, <th> or <td> we have to use otherwise we won't be able to see our table. So <th> or <td> tag they must be wrap in our <tr> tag. We created <th> tag one for name and one for age. Now, data cells are used to fill out the above row.
<table>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Age</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>Rahul</th>
<th>100</th>
</tr>
</table>
To make a table cell span over multiple rows rowspan is used. It can be used as follows:
<td rowspan=value>
Here value is the number of rows u want to span that specific cell
To make a table cell span over multiple columns colspan is used .It can be used as follows:
<td colspan=value>
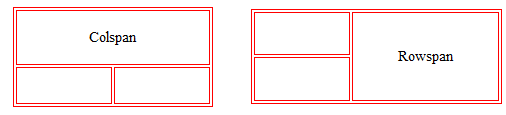
The above picture shows the clear diagramatical representation of attributes rowspan and colspan
Example for colspan:-
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<td colspan=2 >
Merged
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
Third Cell
</td>
<td>
Forth Cell
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
Example for rowspan:-
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<td colspan=2 >
Merged
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
Third Cell
</td>
<td>
Forth Cell
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>